Earthquakes strong and often destructive natural events, have captured the interest of scientists and regular people for hundreds of years. Knowing the natural reasons for earthquakes can give us useful insights into how our planet works. This article explores the main factors that cause earthquakes answering common questions and providing key information on this interesting subject.
What Causes Earthquakes ?
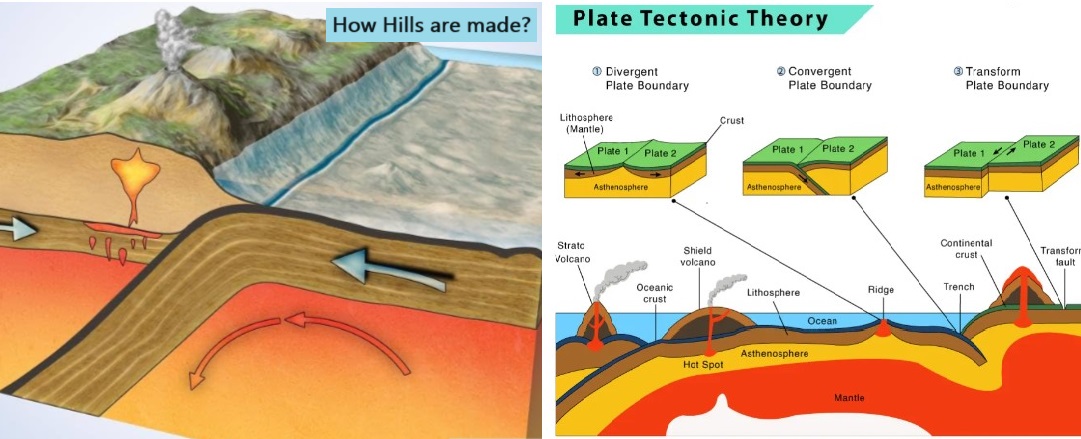
Tectonic Plate Movements
The main natural cause of earthquake has an impact on the movement of tectonic plates. These huge slabs of Earth’s outer layer move though , on the planet’s hot inner layer. When these plates crash into each other, slide past one another, or move apart, they create stress along their edges, which leads to earthquakes.
What are the main types of tectonic plate boundaries?
- Convergent Boundaries: Plates move towards each other causing one plate to sink beneath another, creating subduction zones.
- Divergent Boundaries: Plates move apart forming new crust as magma rises to the surface.
- Transform Boundaries: Plates slide sideways past each other generating friction and stress.
Also Read: What is Project 2025?: Amerifcan Politics
Recent Earthquake Activity
On Tuesday night, an earthquake of a magnitude 5.2 struck close to Lamont, California and travelled across a wide area in Southern California encompassing Los Angeles.

Volcanic activity also has a major impact on earthquakes. Magma movement through the Earth’s crust can put pressure on and break surrounding rocks, triggering volcanic earthquakes. These tremors often happen before volcanic eruptions and can serve as key warning signals.
What’s the difference between volcanic earthquakes and tectonic earthquakes?
- Volcanic Earthquakes: Happen because magma moves and stay close to volcanic areas.
- Tectonic Earthquakes: Come from tectonic plates moving and can happen at different plate edges.
Fault Lines
Fault lines are cracks in the Earth’s crust where stress has pushed parts apart. When these faults move, they cause earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault in California stands out as a well-known example of a transform fault that creates a lot of earthquake activity.
What is a fault line, and how does it lead to earthquakes?
- Fault Line: A break in the Earth’s crust where movement has occurred.
- Earthquake Cause: Movement along these faults lets out built-up stress triggering an earthquake.
Elastic Rebound Theory
The elastic rebound theory sheds light on how energy gets stored and released during an earthquake. As tectonic plates rub against each other stress piles up in the rocks near fault lines. When the stress grows stronger than the rocks, they snap back to their original form sending out energy as seismic waves.
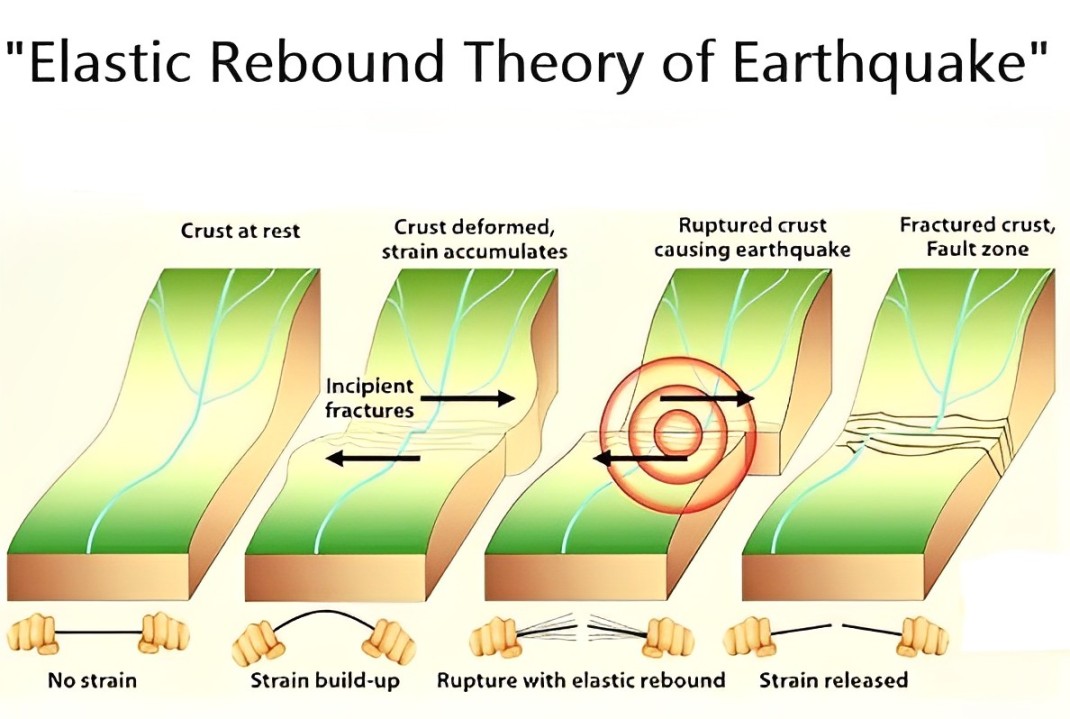
What is the elastic rebound theory?
- Definition: A theory that explains the increase and release of stress along fault lines.
- Significance: Helps us understand why and how earthquakes happen.
Human-Induced Causes
This article looks at natural causes, but we should also mention that human actions can trigger earthquakes. Things like mining building big dams (which causes reservoir-induced seismicity), and fracking change the stress in the Earth’s crust. These changes can lead to earthquakes.
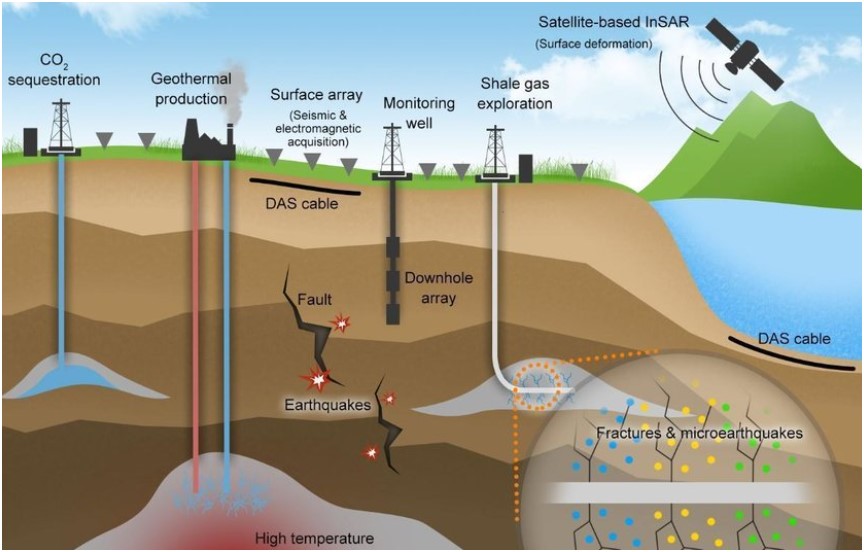
Can human activities cause earthquakes?
- Yes: Mining, fracking, and building dams can make the ground shake.
The Impact of Natural Earthquakes
Global Seismic Zones
Some areas face a higher risk of earthquakes because they sit on the edges of tectonic plates. The “Ring of Fire,” which wraps around the Pacific Ocean, stands out for its frequent earthquakes and volcano eruptions.
Which regions do earthquakes hit the most?
- Ring of Fire: This includes countries such as Japan, Indonesia, and the west coasts of North and South America.
- Other Zones: The Himalayan region, the Mediterranean area, and sections of the Atlantic Ocean.
Earthquakes in History
Over time, earthquakes in nature have wreaked havoc and taken many lives. Studying these events helps us to get ready and lessen their impact.
What are some of the biggest earthquakes in history?
- 1906 San Francisco Earthquake: Destroyed the city and started big fires.
- 2011 Tōhoku Earthquake: Caused a huge tsunami and the Fukushima nuclear accident.
- 1556 Shaanxi Earthquake: The worst earthquake ever recorded killing about 830,000 people.
Earthquake Safety Tips
To stay safe during an earthquake, you need to know what to do before while, and after the ground shakes. Here are some key safety tips:
Before an Earthquake
Make Your Home Safe
- Secure heavy furniture: Attach bookshelves, cabinets, and other bulky items to walls.
- Put in latches: Add safety latches to cabinets to stop contents from falling out.
- Look for dangers: Spot and fix any possible dangers such as loose bricks or shaky fixtures.
Make a Plan
- Create an emergency strategy: Ensure all family members understand what to do in an earthquake.
- Do drills: Often practice earthquake drills, like “Drop, Cover, and Hold On.”
- Learn your escape routes: Get to know the safest and fastest ways out of your home or building.
During an Earthquake
Drop, Cover, and Hold On
- Drop: Get on your hands and knees to stop yourself from falling over.
- Cover: Shield your head and neck under a strong table or desk.
- Hold On: Grip your shelter until the quake ends.
Stay Indoors
- Avoid windows: Keep away from windows, glass, and outer walls.
- Stay put: If you’re inside, remain there. If you’re outside, find an open area far from buildings, trees, and power lines.
After an Earthquake
Look for Injuries and Damage
- Check for injuries: Give first aid to hurt people and get professional medical help if needed.
- Look over your house: Search for damage to the structure, gas leaks, and problems with electricity.
Keep Up with News
- Tune in for updates: Use a radio that runs on batteries to hear emergency info and news.
- Don’t travel if you don’t have to: Roads and bridges might be broken, so stay where you are unless it’s not safe.
Kit for Earthquake Emergencies
A kit for earthquake emergencies can save your life after the ground shakes. Here’s what you should put in it:
Must-Have Items
- Water: Each person needs at least one gallon of water a day for three days minimum.
- Food: Stock up on food that won’t spoil for at least three days.
- First aid kit: Pack bandages, antiseptics, meds, and other medical stuff.
- Flashlight: Don’t forget extra batteries.
- Radio: Get one that runs on batteries or has a hand crank.
- Multi-tool: You’ll need this to turn off utilities and do quick fixes.
Additional Supplies
- Blankets and clothing: Stay warm and dry.
- Personal hygiene items: Pack soap, toothbrush, and sanitary products.
- Important documents: Pack copies of ID, insurance papers, and emergency contacts.
- Cash: Bring small bills.
Custom Items
- Baby supplies: Pack diapers, formula, and baby food.
- Pet supplies: Pack food, water, and pet medicines.
- Prescription medications: Pack needed medicines.
Earthquake-Prone Areas
Knowing if you live in an earthquake-prone area helps you prepare. Here are some of the most active earthquake regions:
Global Earthquake Zones
Ring of Fire
- Location: Surrounds the Pacific Ocean.
- Countries Affected: Japan, Indonesia, New Zealand, and the western shores of North and South America.
- Characteristics: High levels of volcanic and earthquake activity.
Himalayan Region
- Location: Extends across India, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- Characteristics: Strong earthquakes happen often because tectonic plates crash together.
Mediterranean Region
- Location: Covers countries such as Greece, Turkey, and Italy.
- Characteristics: Earthquakes occur due to complex interactions between tectonic plates.
U.S. Earthquake Zones
California
- Major Fault: San Andreas Fault.
- Cities Affected: Los Angeles, San Francisco, San Diego.
- Characteristics: Many earthquakes happen here, and big ones might occur.
Pacific Northwest
- Major Fault: Cascadia Subduction Zone.
- Cities Affected: Seattle, Portland.
- Characteristics: Large earthquakes and tsunamis could happen.
Alaska
- Major Fault: Denali Fault.
- Characteristics: Strong earthquakes often occur due to plates moving against each other.
The Earth’s inner workings cause most earthquakes. These include the movement of tectonic plates, volcanoes erupting, faults in the ground, and something called elastic rebound. When we know more about these natural events, we can get ready for earthquakes and lessen their effects. To stay safe, it’s a good idea to learn about what makes the ground shake in different parts of the world.

