A healthy diet majorly made up of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables is one without which dietary fiber cannot be said to exist, is a vital part of one’s diet. Made up of the undigested portions or elements of plants, it goes through our intestines and stomachs almost the same way it went in.
While fiber is sugar but its function is exclusively involved in keeping the stomach area healthy and aiding in digestion. It is commonly known as bulk or roughage and exists in various types some being water-soluble yet not bulky or rough at all. Here we begin to explore the dietary fiber and it’s related factors.
Different Types of Dietary Fiber
Dietary fiber comes in two primary types: soluble and insoluble, with both forms being essential in maintaining good nutrition hence they are encouraged on a daily basis.
Soluble Fiber: This type of fiber absorb the water like a sponge and it helped to bulk out stool so it can pass through the gut more easily. Reducing digestion is another factor that slows it down, thus reducing the levels of ‘bad cholesterol‘ or LDL. Psalm adulteration gives the entire context in which these sources of it occur.
Insoluble Fiber: Insoluble Fiber does not absorb water and speeds up the movement of food through the stomach. So, these types of fober helps to prevent from constipation. Among the sources of carbohydrates, cellulose can be found in wholegrain foods, nut skins, fruits, and seeds, as for hemicelluloses, they are found in bran, cellulose, and potato tubers’ starch granules.
Resistant Starch: Resistant starch behaves in similar ways even if it is not classified as fiber traditionally. Human small intestines cannot digest it yet it undergoes fermentation in the colon which may improve colon health or prevent colon cancer. It can be found in wholegrain, unripe bananas, potatoes and legumes standing for good sources of this type of carbohydrate.
Health Benefits of Dietary Fiber
There is many benifits of dietary fiber if you include your meal, by following the dietary fiber. Here are the major health benifits if you would be aware about this dietary fiber:
Digestive Health: Fiber helps add bulk to stool and makes sure that the digestive system remains in a healthy state so that there is a lower risk of constipation, haemorrhoids, and diverticulitis.
Weight Management: Foods with high-fiber content are usually less dense in energy, which implies that they give out fewer calories in every gram. Additionally, they create a sense of fullness thereby controlling hunger hence aiding in checking weight gain.
Blood Sugar Control: Fiber is known to reduce how quickly glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream in patients suffering from diabetes hence averting instances where people experience abnormally high glucose levels while at the same time aiding them in controlling insulin production.
Heart Health: Soluble fiber lowers total and LDL cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of coronary heart disease. It does this by binding bile acids (made from cholesterol) and excreting them from the body.
Cancer Prevention: Fibers increases the intestines size, making potential dietary carcinogenic agents less concentrated in the intestines and lowering duration required for food transit through there, thus helping to decrease bowel cancer threats (Lusas, 1989). There are also some referrals that high fiber diets might lower chances of developing breast carcinoma as well.
Healthy Ageing: With our increasing age, digestive system slows that makes it important to eat high fiber as this can help us prevent constipation. Also it helps to maintain a healthier digestive system.
What has happened if we eat just Low-Fiber Diets?
A diet low in fiber has been associated with various health issues, including:
- Constipation
- Haemorrhoids
- Diverticulitis
- Breast cancer
- Bowel cancer
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Overweight and obesity
Recommended Daily Fiber Intake
Many adults do not consume enough fiber, which their body needs. The popular recommendation of daily intake is 30g for men and 25g for women. And for children, it varies from 18g to 28g depending on their age, gender and body weight .
Simple Ways to Increase Your Fiber Intake in your meal
- You should always choose breakfast cereals that contain barley, wheat, or oats.
- Try to switch to wholemeal or multigrain bread and brown rice.
- You have to add an extra vegetable to every evening meal.
- Take the snack on fruits, dried fruits, nuts, or wholemeal crackers.
One can consume wholegrain cereals, fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes and nuts or seeds instead of eating snacks low in dietary fiber that would usually help in achieving more than 30 gram intake within a day.
Why is Dietary Fiber Important for the Body?
Enough consumption of fiber has connection to less chances of getting sick from persistent ailments such as obesity-related cases, diabetes type II, cardiovascular illnesses among others (Rees 2012). This is because; cholesterol levels are lowered by soluble fiber (Bruno 2012).
Moreover, both types of fiber i.e., insoluble fibers which are found in bran cereals, skins fruits and some vegetables while soluble ones including oat bran also contribute to improved blood sugar management hence lowering incidences of diabetes type II”(Smith et al 2010).
Fiber also plays a vital role in digestive system of our body by preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. Also a high-fiber diet supports to manage the weights. Fiber rich foods, include fruits like apples and berries, vegetables such as carrots and broccoli, whole grains like oat bran and brown rice, legumes including beans and lentils, and nuts and seeds such as almonds and flaxseeds.
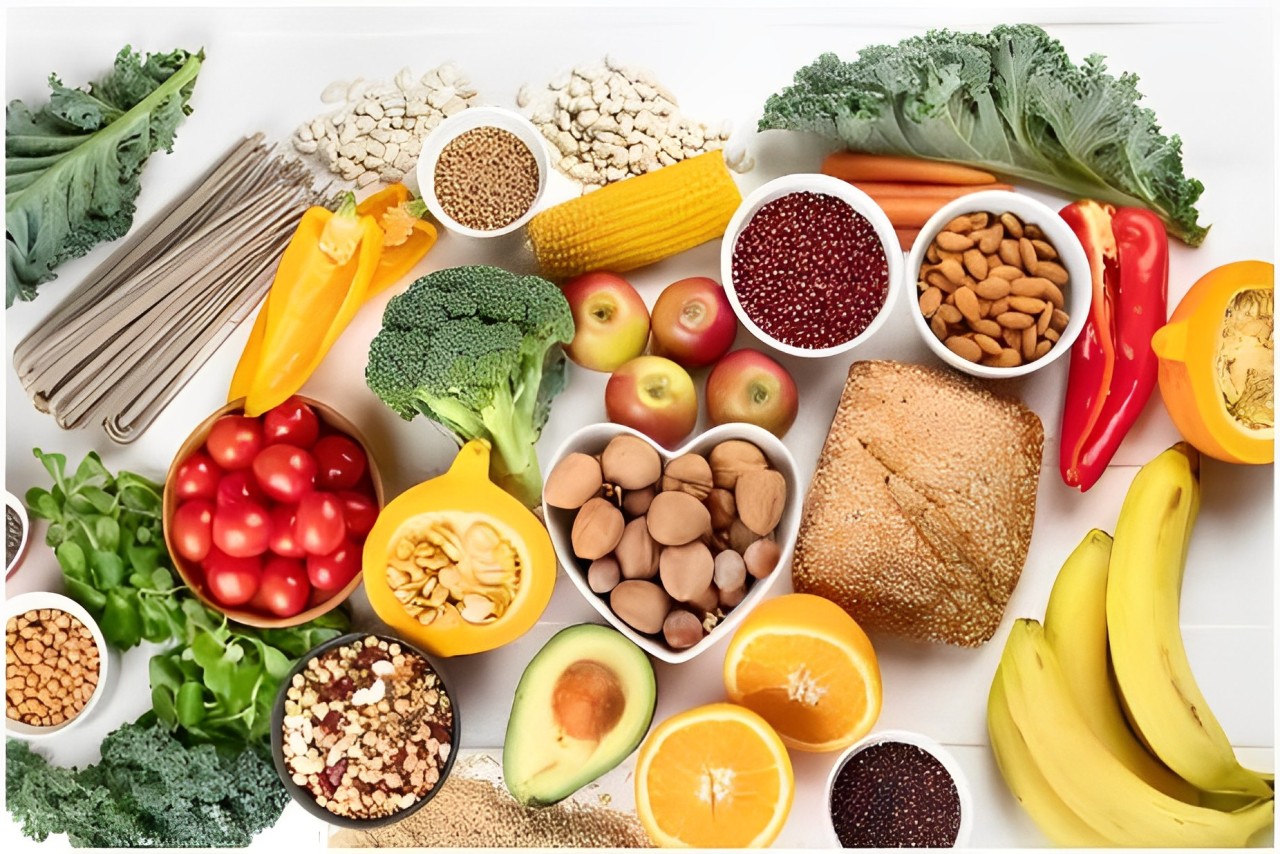

With these fiber-rich foods into your diet is essential for promoting better health and preventing many chronic diseases.
What are the high fiber foods?
- Fruits: Apples, berries,oranges,pears and bananas.
- Vegetables: Carrots, sweet potatoes, broccoli and peas.
- Whole Grains: Oat bran, brown rice, barley and whole wheat bread.
- Legumes: Beans, chickpeas and lentils.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, flaxseeds, and sunflower seeds.
Adding more roughages to your daily menu is among the most significant things that you can do to maintain a better health. Although fiber-rich food helps lower chances of chronic diseases, aids in loss of weight, and enhances digestion. Take advantage of these advantages by making roughages a must-eat-with food every day.
Please don’t forget to rate this article through the reaction, Thank you.

