In the southwestern part of Iceland, the Reykjanes Peninsula has had another big volcanic eruption which is a continuation of volcanic activities that started since December 2023. This current eruption started on May 29 2024 with lots of lava coming out from it as well as massive geological changes taking place.
Volcano Eruption Details of Iceland
During the initial phase, the volcanic fissure, which is known for its vigorous lava flows near the town of Grindavík, was reactivated by the eruption. This eruption began at a speed that has never been seen before. Its earliest lava flow rates were measured to be up to 1,500 cubic meters per second as per NASA Earth Observatory.

According to recent information from the Icelandic Meteorological Office (http://www.vedur.is), lava is mostly moving in a north/western direction from one vent (Sylingarfell) and southwards from another called Hagafell.
Environmental and Health Impact of Volcano
Significant gas pollution from the eruptions has become a major worry for places like Grindavík situated near to the volcano (Icelandic Meteorological office) (NASA Earth Observatory).
These notherly winds take greenhouses gases in the southward direction which may compromise breathing air with a need for constant surveillance on gas concentration levels in individual locations. The advice given to the people living or visiting areas under threat is that they should not go out when the level is up.
Geological Observations
Svartsengi has been effected by the volcanic eruption that resulted in material displacement on the earth’s surface as well as fuel markdown. In the beginning, the low-lying ground sank which led to the thought that the outflow of more magma than what was getting into the underground chamber took place.
Nevertheless, the most recent statistics confirm that the depression stopped happening place while the movement of fuel slowed down (Icelandic Meteorological office)
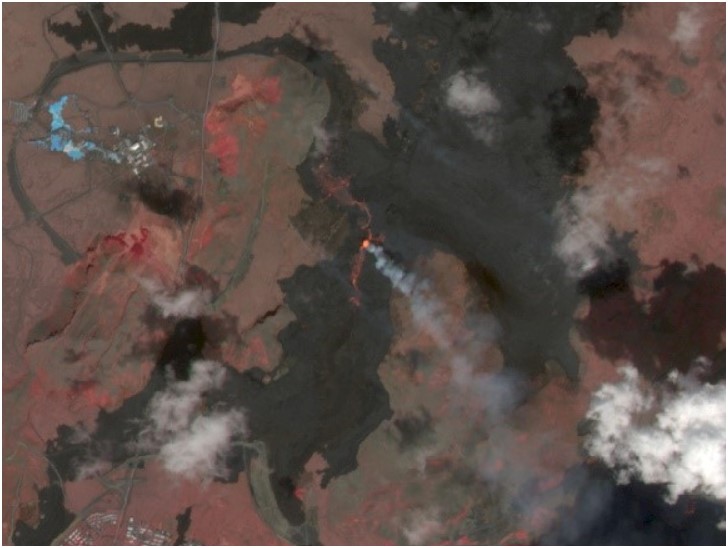
The satellite images and thermals have actually been very crucial in showing the advise the flow of magma and heat spots. It is estimated that the lava field now covers about 8.6 square kilometers. While its volume is estimated at approximately 36 million cubic meters (Icelandic Meteorological office). This is because the lack of major ash emissions from this eruption has meant no significant disruptions to air travel (NASA Earth Observatory)
Community Impact
Grindavík remains highly vigilant because it was mostly abandoned since late 2023 due to erupting volcanoes that never stopped. This has made it difficult for them to rebuild their lives or go back to normalcy without any support.
Whatever from outsiders like Americans who would have helped them financially throughout those years otherwise on end making it even better than it is now. Since things might have been different had they not been available at that time (NASA Earth Observatory).
Geological and meteorological agencies are keeping a close eye on volcanic activity in Reykjanes Peninsula. To guarantee safety, as well as evaluate the dynamic geological statuses, the Iceland Meteorological Office among other institutions makes regular updates.
There is need for additional research in view of the fact that will help to comprehend better this landscapes and communities in the long run in terms of volcanic event on the region.
You can see real-time updates and detailed information about the eruption using the Icelandic Meteorological Office’s website and some other preferred news sources.

