Sodium-ion batteries (NIBs) were originally developed in the early 1980s. It has emerged as a promising contender. These batteries, utilizing sodium ions instead of the more conventional lithium ions, hold the potential for lower costs, greater abundance of raw materials, and reduced environmental impact. As the world seeks alternatives to lithium-ion batteries, sodium batteries offer a glimpse into a future of more accessible and eco-friendly energy storage options.
Although not yet prevalent in the automotive industry, sodium batteries are garnering attention for their potential use in electric and hybrid vehicles. Challenges such as optimizing energy density, cycle life, and compatibility with existing charging infrastructure need to be addressed before widespread adoption can occur.
What is Sodium Batteries made of?
Sodium, abundant and widely distributed, presents a more sustainable option than lithium, which is less plentiful. This abundance suggests that sodium batteries could be more cost effective and environmentally friendly in the long term. There are several key components for make the Sodium Battery useable, here it is:
- Anode: The anode is the negative electrode of the battery, where the process of discharging (or releasing) electrons occurs during battery operation. In sodium batteries, the anode is typically made of a material capable of intercalating or absorbing sodium ions, such as hard carbon or sodium titanate.
- Cathode: The cathode is the positive electrode of the battery, where the process of accepting electrons occurs during battery operation. In sodium batteries, the cathode is typically made of a material capable of intercalating sodium ions, such as sodium metal oxides (e.g., sodium cobalt oxide, sodium nickel oxide) or polyanionic compounds (e.g., sodium iron phosphate).
Also read: Introducing the Sustainability and future of AI Robots: Debunking Myths and Exploring Possibilities
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a conductive solution or solid material that allows ions to move between the anode and cathode during battery operation. In sodium batteries, the electrolyte contains sodium ions dissolved in a solvent or embedded in a solid matrix, facilitating the flow of ions and the transfer of electrical charge.
- Separator: The separator is a porous membrane that physically separates the anode and cathode while allowing the flow of ions between them. The separator prevents short circuits and ensures the efficient operation of the battery.
- Current Collectors: Current collectors are conductive materials that collect and transport electrons generated during battery operation. They are typically made of metals such as copper or aluminum and are attached to the electrodes to facilitate the flow of electrical current.
These components work together in a sodium battery to store and release electrical energy through the reversible electrochemical reactions of sodium ions between the anode and cathode.
How much does the Sodium Battery Cost?
Sodium batteries have the potential to be more affordable than lithium batteries due to the abundance of sodium resources and potentially lower manufacturing costs. However, as per the reports of IDTechEx, the average cost of a sodium-ion battery cell is $87 per kilowatt/hour. However, a sodium scooter battery pack can cost as little as $18.24 in cells, which is much cheaper than the more than $300 cost of a Honda Motocompacto battery.
Sodium battery cost in different Nations:
United States = $90 /KW
Germany = €129 and €149
India = $100/KW
China = $77/KW
United Kingdom = $77 KW
Energy Density of Sodium Battery
While lithium batteries typically boast higher energy density, allowing them to store more energy in a smaller space, sodium batteries offer a promising alternative with ongoing advancements in technology. However the theoretical capacity of a sodium-ion battery is around 170 mAh/g, which is split between two one-electron voltage plateaus. Sodium metal has a theoretical capacity of 1165 mAh g−1.
How long does Sodium Battery last? Life spam
Lithium batteries often outlast sodium batteries in terms of cycle life, meaning they can endure more charge-discharge cycles before their capacity significantly diminishes. Its key attributes include 3000–6000 cycles longer lifespan, quicker charging compared to regular batteries, better resilience in freezing weather conditions and various energy densities ranging from 100 to 170 Wh/Kg.
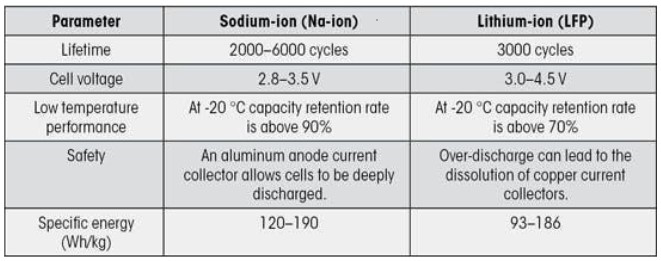
How safe is Sodium Batteries than Lithium Batteries?
While both sodium and lithium batteries carry safety risks, sodium batteries are considered safer in some regards due to the lower reactivity of sodium compared to lithium. This sodiuum batteries can discharged to zero volts when it needed to transport or storage, so it seems more safer than other batteries. Also it has the lower risk of flammability than Lithium.
Manufacturing Companies
Several companies and research institutions are actively involved in sodium battery development, from established industry giants to startups focusing specifically on sodium battery research and production. CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd.), which is founded in 2011 and located in Ningde, Fujian Province, China is one of the top and largest manufacturing company of Sodium Battery. Others manufacturing companies are as follows:
- Faradion, UK
- HiNa Battery Technology Co, Ltd., China
- Natron Energy, inc., United States
- Tiamat Sas, France
- AGM Batteries Ltd, United Kingdom
- Faradion Ltd (Reliance), UK
- Altries, Sweden
In India, Sodion Energy is the first company, co-founded by Bala Pachyappa which is manufacturing different type of Sodium-ion batteries.
News
News surrounding sodium battery technology often highlights advancements in research and development, breakthroughs in manufacturing processes, partnerships between companies and research institutions, government initiatives supporting sodium battery research, and potential applications in various industries.
Will Sodiuym Batteries Replace with Lithium Batteries?
This is one of the most curious question, nowadays. We have to compare the sodium batteries with another to know this. As we know that, Sodium batteries are much safer than lithium. In the test of Dodium battery, such as , discharge, Short circuit, Acupuncture etc. the output result are shocking and this seems more safe than lithium. Also the cost of the Sodium batteries is 30% lower than lithium.
Reducing dependence on lithium resources and developing new low-cost and high-safety battery systems have always been the driving force behind the inexhaustible exploration of sodium batteries. However, the large ion radius means that sodium batteries have innate shortcomings in energy density. As a result, backup power supplies, low speed electric vehicles, energy storage, and all other scenarios where lead-acid batteries are being used will become the home field that sodium batteries will soon occupy.
Also read: The Best Virtual Reality Headsets of 2024: Unveiling the Ultimate Virtual Reality Experience
| Feature | Sodium Battery | Lithium Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Availability | Abundant and widely available sodium resources | Limited and less abundant lithium resources |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to abundance of sodium resources | Higher due to scarcity of lithium resources |
| Energy Density | Lower compared to lithium batteries | Higher, allowing for greater energy storage in a smaller space |
| Cycle Life | Generally shorter lifespan | Longer lifespan, enduring more charge-discharge cycles |
| Safety | Considered safer due to lower reactivity of sodium | Some safety concerns due to flammability and reactivity |
| Application | Emerging technology, potential use in electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage | Widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems |
| Development Status | Still in research and development phase | Mature technology with ongoing advancements |
Additionally, the increasing demand for energy storage solutions, particularly in renewable energy systems and electric vehicles. It may drive the adoption of sodium batteries as a complementary or alternative technology to lithium-ion batteries. Ultimately, the future role of sodium batteries will be influenced by a combination of technological advancements, market dynamics, and regulatory factors.
Dear readers, If you hage any message or suggestion for us, please message us on sharpinn.com. Thank you.